
How High Do Drones Fly? (And why it doesn’t matter!)
How high can drones fly? Well, we leave no stone unturned in answering exactly that! From hobbyists, to commercial and military drones too.
As the agricultural industry continues to evolve, one of the most significant advancements has been the integration of agricultural drones benefits for modern farming practices. UAVs are revolutionising precision farming, providing growers with exact and timely info for effective decision-making.
In this blog post, we’ll delve deeper into how drone technology is transforming the agricultural sector. We will discuss various roles drones play in agriculture industries and precision agriculture, such as real-time data collection and monitoring crop health. Additionally, we will explore some main benefits of using drones in agriculture including cost-effectiveness and increased accuracy.
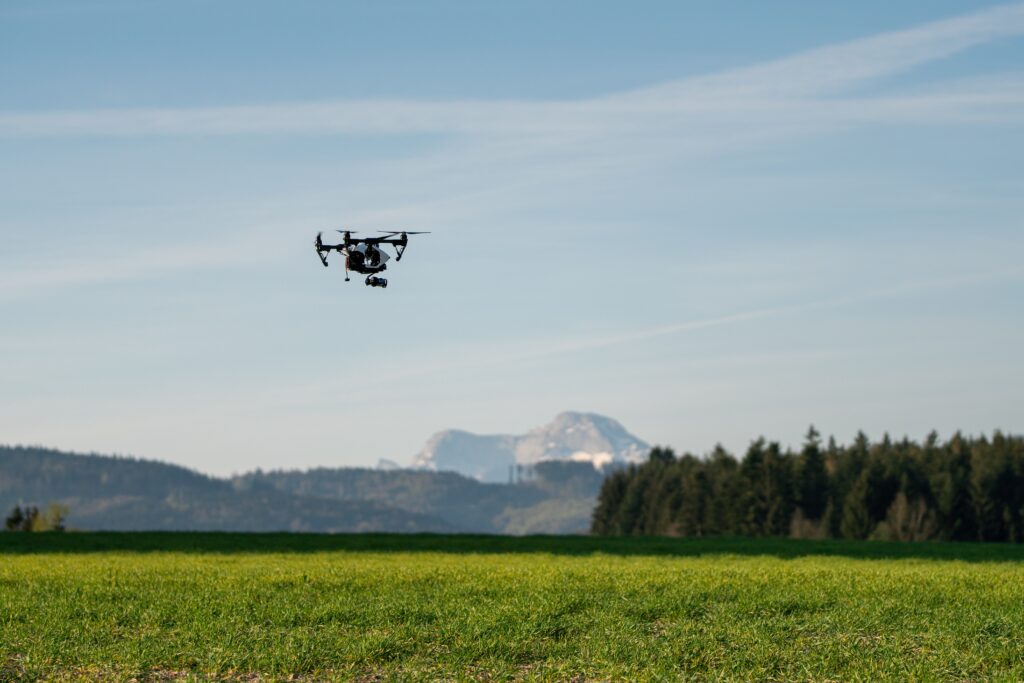

Drones are changing the game in precision agriculture, helping farmers increase yields and manage their farms more efficiently. By utilising drone technology, farmers can obtain up-to-date information and make judicious choices regarding crop health and management, as well as monitor livestock. Let’s explore how drones are revolutionising the agricultural sector.
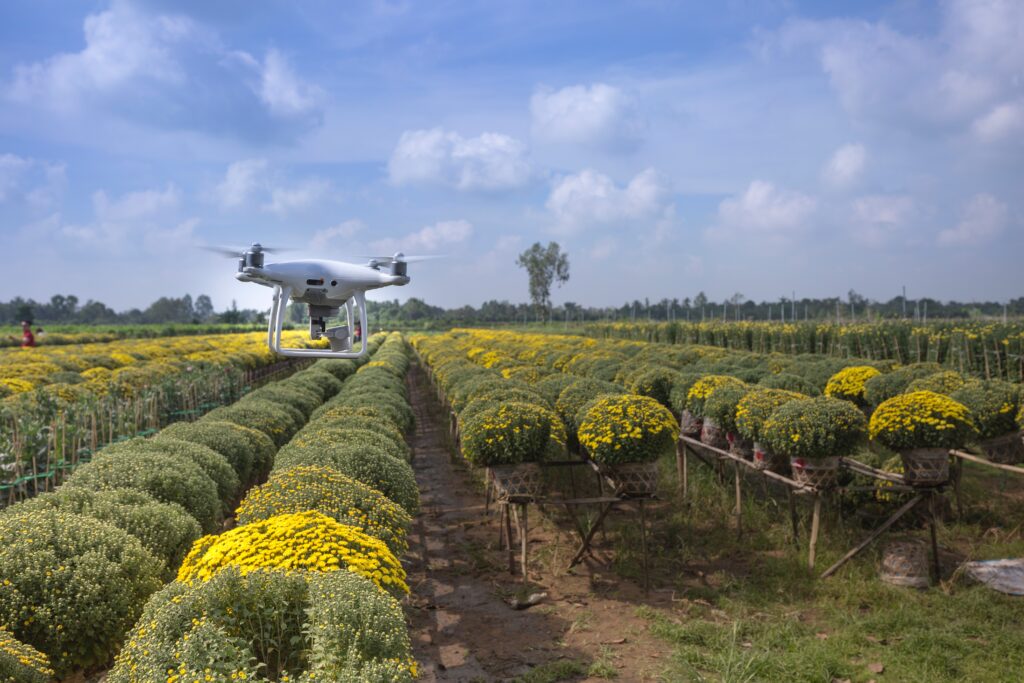

One of the main benefits of using agricultural drones is their ability to collect data quickly and efficiently. Equipped with advanced sensors, many drones used in agriculture now can cover large areas in a short amount of time and gather data, providing farmers with critical information about their crops. This allows for informed decision-making on irrigation scheduling, nutrient management, and pest control strategies.
With multispectral imaging techniques like NDVI, drones can also identify potential issues early on, before they become major problems. This helps farmers take action to prevent yield losses and ensure a successful harvest.
Drones equipped with thermal cameras and other sensors are particularly useful in monitoring crop health and identifying issues early. By using weather conditions and capturing high-resolution images of temperature variations across a field, farmers can detect the presence of pests and diseases before they spread. This allows for effective intervention measures to be taken without causing harm to the crop quality surrounding ecosystem.
Precision agriculture techniques involving drone technology are also useful in monitoring soil moisture levels and assessing water stress conditions among crops. By using soil conditions and identifying areas of crops that require additional irrigation or improved drainage systems, farmers can optimise their water usage while ensuring optimal growth conditions for their plants and crops.
In conclusion, drones are transforming the agricultural sector by providing real-time data collection and enabling farmers to monitor crop health more effectively than ever before. This not only improves farm productivity but also promotes sustainable agricultural practices. As drone technology continues to advance, we can expect even greater benefits from drone use for the agricultural sector in the future.
Farmers are increasingly adopting drones as part of their agricultural practices due to numerous benefits that directly impact productivity and efficiency. These benefits include cost savings, increased accuracy, reduced environmental impact, and improved overall farm management. In this part, we will examine the various advantages of using drones for farming in more depth.
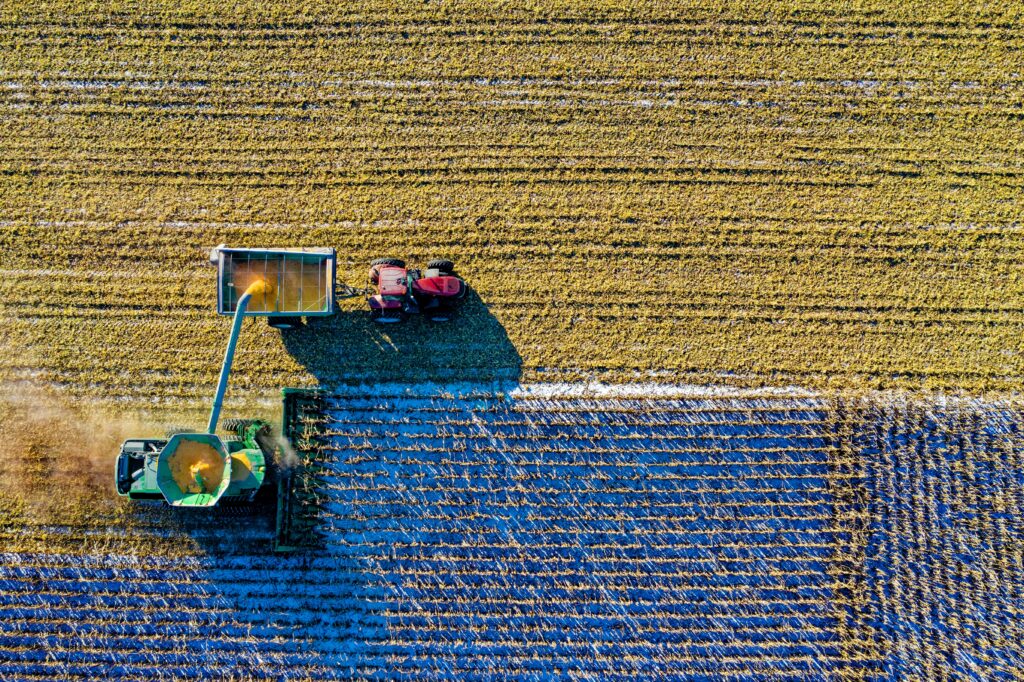

Agricultural drones offer a more affordable alternative to conventional methods such as manned aircraft or satellite imagery for monitoring crops. The initial investment required for purchasing a drone is significantly lower than the costs associated with hiring pilots or paying for satellite services.
Additionally, drone operators can perform multiple tasks at once without needing extra manpower on the ground, resulting in further cost reductions. Studies have shown that using drones can save farmers up to 85% on various operational expenses when compared with traditional techniques.
Drones equipped with advanced sensors and cameras can collect high-resolution images and data from fields quickly and accurately. This information allows farmers to make informed decisions about crop planting strategies, irrigation systems, fertiliser application rates, pest control measures among other things – all based on real-time insights provided by their unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
The use of agricultural drones contributes significantly towards mitigating negative impacts upon our environment too. For instance, UAVs allow for more efficient water management practices through precise irrigation scheduling based on real-time data collected from fields thereby conserving this precious resource as well ensuring optimal growth conditions exist throughout entire growing season (source).
Moreover, since these unmanned aircraft systems require lesser amounts fuel compared traditional manned vehicles like tractors airplanes etc., their carbon footprint remains considerably lower overall thus promoting greener farming methodologies worldwide.
Furthermore, drone technology facilitates easier livestock monitoring helping track animal movements grazing habits effectively without disturbing them or harming crops unduly so that appropriate interventions may be implemented timely manner if required thereby enhancing welfare standards for many farmers within sector at large.
Farmers have a variety of drones at their disposal, each designed to cater to specific needs and requirements within the agriculture industry. UAVs provide farmers with a range of useful capabilities, such as tracking crop growth or controlling livestock. In this section, we will explore three main types of agricultural drones: fixed-wing drones, multi-rotor drones, and hybrid VTOL (Vertical Takeoff & Landing) drones.
Fixed-wing drones are known for their long flight times and ability to cover large areas quickly. They are ideal for mapping vast expanses of farmland or conducting aerial surveys in search of optimal planting locations. Equipped with high-res imaging and multi-spectral detectors, these UAVs can generate precise visuals that enable farmers to take educated guesses when it comes to planting plans.
In contrast to fixed-wing models, multi-rotor drones, which include quadcopter’s and hexacopter’s among others, excel in manoeuvrability thanks to their multiple rotors allowing them to hover over a particular area while capturing high-quality imagery from various angles. This makes them perfect for tasks that require precision, such as monitoring a crop’s health or spraying pesticides in a targeted manner.
The third category of agricultural drones is the hybrid VTOL (Vertical Takeoff & Landing) drone, which combines the best features of both fixed-wing and multi-rotor UAVs. These versatile flying drones that can take off vertically like a helicopter before transitioning to horizontal flight mode, allowing them to cover large distances quickly while still maintaining excellent stability during hover operations. As a result, they are well-suited for use in diverse farming activities ranging from crop scouting to livestock monitoring.
Modern agricultural drone systems utilise advanced technologies that not only capture high-quality images but also analyse these datasets, providing valuable insights into various aspects related to farming activities. These cutting-edge tools help improve overall performance significantly over time while minimising negative impacts on the environment, thereby promoting sustainable development goals achievement globally. In this section, we will discuss some of the key technologies used by agricultural drones and their applications.
Multispectral sensors are one of the most important components in agriculture drones as they enable them to capture data across different wavelengths of light. This information is crucial for assessing crop health, soil quality, and detecting pests or diseases early on. By analysing multispectral imagery captured by drones equipped with these sensors, farmers can make informed decisions about irrigation scheduling, fertiliser application rates, and pest management strategies.
Drones equipped with thermal cameras allow farmers to monitor temperature variations within their fields more effectively than traditional methods such as ground-based measurements or satellite imagery alone. Thermal imaging helps identify areas where crops may be experiencing water stress due to insufficient irrigation or drainage issues. Additionally, it can detect heat signatures from livestock animals which could indicate potential health problems requiring immediate attention.
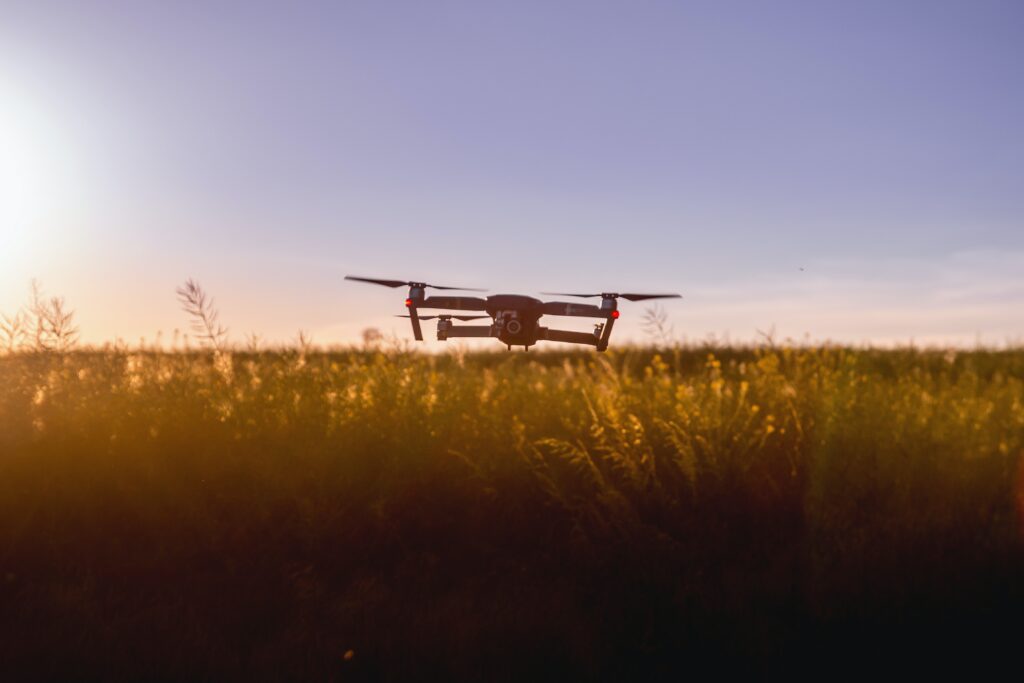

Agricultural drone operators rely heavily on GPS-guided flight planning software for efficient mission execution and accurate data collection. These solutions enable UAVs to adhere to pre-set paths, ensuring complete coverage of the inspected area and diminishing the likelihood of overlooking essential details. Moreover, GPS-guided software allows for precise geolocation tagging of collected data, making it easier for farmers to pinpoint problem areas within their fields.
Lidar sensors, which use laser technology to measure distances and create detailed 3D maps, are becoming increasingly popular in agricultural drone applications. These high-resolution maps can be used for various purposes such as topographic analysis, crop planting planning, and monitoring infrastructure like irrigation systems or fences.
Lidar-equipped drones also have potential uses in precision agriculture by providing accurate measurements of plant height and canopy density – essential factors when determining optimal harvesting times or estimating yields.
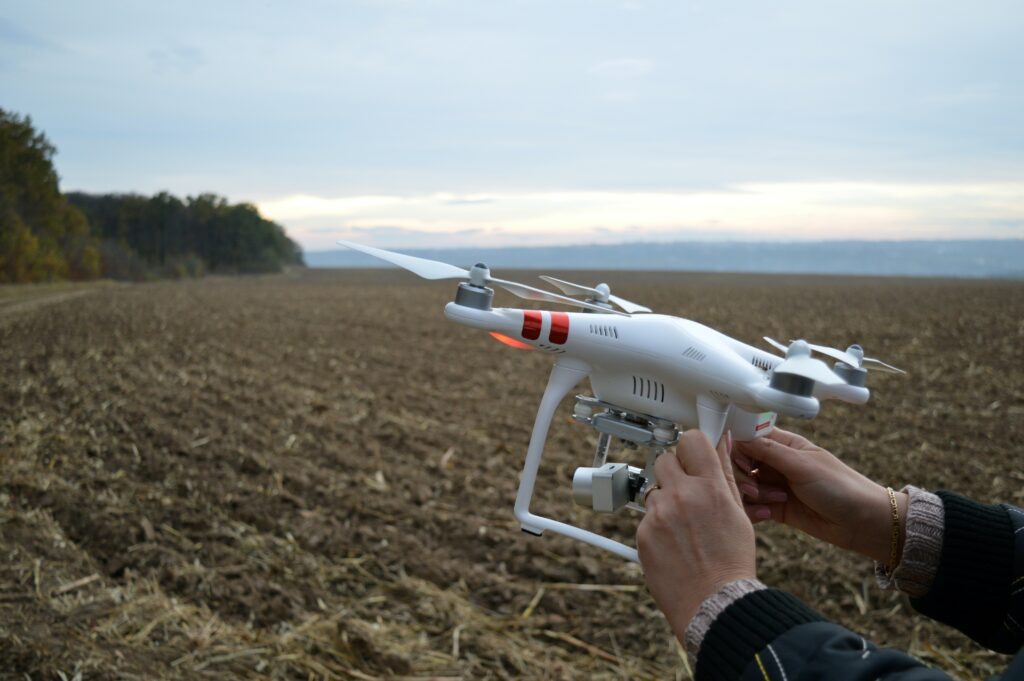

Using agricultural drones is a game-changer for farmers and businesses, providing real-time data collection and crop monitoring capabilities that make precision agriculture more accessible and cost-effective than ever before.
With the ability to collect accurate information and identify issues early on, farmers can make informed decisions that lead to better crop yields, and reduced use of chemicals, helping to preserve our environment.
From fixed-wing drones for aerial surveillance and large-scale mapping operations to multi-rotor drones for detailed imaging and precise spraying applications, there are different types of agricultural drones available to suit various farming needs.
Investing in this technology is a smart move for any farmer looking to optimise inputs and increase accuracy in data collection, leading to better outcomes and a more sustainable future.
Related Post’s

How high can drones fly? Well, we leave no stone unturned in answering exactly that! From hobbyists, to commercial and military drones too.
How Far Can Drones Fly? Learn about flight times, legalities, and drone usage across industries here in this article.

Navigate New York drone laws with confidence. Understand federal, state, and local regulations for safe commercial and recreational drone use.