
How High Do Drones Fly? (And why it doesn’t matter!)
How high can drones fly? Well, we leave no stone unturned in answering exactly that! From hobbyists, to commercial and military drones too.
From a technical perspective, the complexities and capabilities of many drones, are vast. In this article, we will look at future drones uses and definition, providing a better understanding for both novice enthusiasts and seasoned professionals alike.
Let’s explain a drones uses and definition for what exactly constitutes as a drone or an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). Exploring their varying levels of security vulnerabilities, of autonomy, traveling capabilities, and how drone operators control these sophisticated machines.
In our exploration of different types & uses of future drones, we examine everything from very close range UAVs to endurance models used for extended missions. Including the role that these aerial vehicles play in diverse fields like search & rescue operations, police & scientific research.

Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, have revolutionised the world with their advanced capabilities and wide range of applications. Professionals in a variety of fields have come to rely on drones for their versatility and sophisticated capabilities.
A drone, at its most basic level, is an aircraft without a human pilot on board. It can be remotely controlled or fly autonomously through software-controlled flight plans embedded in their systems working in conjunction with onboard sensors and GPS.
The levels of autonomy for drones vary greatly depending on their intended use. Some drones require full control from remote operators while others operate semi-autonomously needing minimal human operation during flight. Most advanced UAVs are fully autonomous, capable of performing complex operations independently once programmed with specific instructions.
Fully Manual: These drones need constant input from the controller throughout the entire flight duration.
Semi-Autonomous: Semi-autonomous models can perform certain tasks like takeoff or landing automatically but still require manual control for navigation.
Fully Autonomous: Fully autonomous UAVs carry out all aspects including takeoff, navigation & landing without any human interference after initial programming.
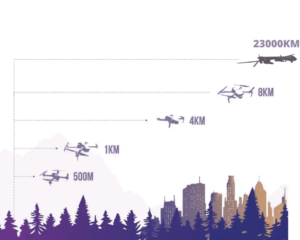
The traveling capabilities differ based on drone type and purpose. For instance, consumer-grade quad-copters might only travel several hundred feet vertically whereas high-end commercial grade units could reach altitudes up to thousands of feet above ground level (AGL).
Similarly, distance coverage varies from a few miles for smaller models up to hundreds of miles for larger ones equipped with sophisticated technologies. FAA regulations, however, limit recreational drone flights under 400ft AGL within visual line-of-sight (VLOS).
In essence, understanding these basics about drones helps us appreciate not just how far we’ve come technologically but also gives insight into potential future advancements this industry holds.

When it comes to availability on the drone market, there is a vast selection to suit different requirements and objectives. From hobbyist activities to military operations, the applications are as diverse as the types themselves. Let’s delve into some common categories of these unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
These tiny drones are perfect for beginners exploring future drone technology. They’re compact, easy to manoeuvre, and great for basic surveillance tasks. This type of drone can cover a maximum distance of 5 km in the air for up to an hour, making them ideal for basic surveillance.
For more demanding tasks such as detailed land surveys or wildlife monitoring, close-range UAVs are the way to go. With a flight radius between 50km -150km and endurance levels reaching three hours, they’re up for the challenge.
Short-range drones and other types of drones are primarily used by military forces and government agencies for espionage purposes, often being piloted remotely.
With an impressive flight radius extending up to 300 km as well as a six-hour endurance time, they offer exceptional reconnaissance gathering abilities sometime via artificial intelligence, without risking human lives on dangerous missions, whether its for mission planning, intelligence gathering, or to deliver a lethal or nonlethal payload.
Mid-range UAVs serve well in research contexts where extensive data collection is required over large areas like climate studies or geographical mapping projects. Also, they can cover distances up to 650 km over eight hours.
Endurance UAVs are the giants among drones and aircraft. These heavy-duty machines can cover whopping distances exceeding 3000 km while staying aloft for over thirty-six hours. This makes them perfect candidates when long-distance aircraft travel is needed such as international cargo transport or high-altitude weather observation missions.
To summarise: Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned professional, there’s undoubtedly a drone out there tailored perfectly to meet your specific requirements.

Drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), have become increasingly popular over the years. Initially developed for military purposes, drones are now being used in various fields such as:

Drones have become increasingly popular in recent years. They are no longer just a tool for the military; drones are now being used by businesses of all sizes for commercial purposes.
There is a difference between consumer-grade drones designed for hobbyists and professional-grade drones designed for commercial use. Consumer drones are typically less expensive, smaller in size, and easier to operate than their professional counterparts.
Professional drones often have more advanced features like longer battery life, higher quality cameras, and greater stability in windy conditions. They also require a license from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) to operate commercially.
No matter what type of drone you choose as your hobby or interest, it’s essential to follow safety guidelines set by FAA regulations. The FAA has strict rules on where you can fly your drone and how high it can go up into the airspace before risking other aircraft’s safety issues.
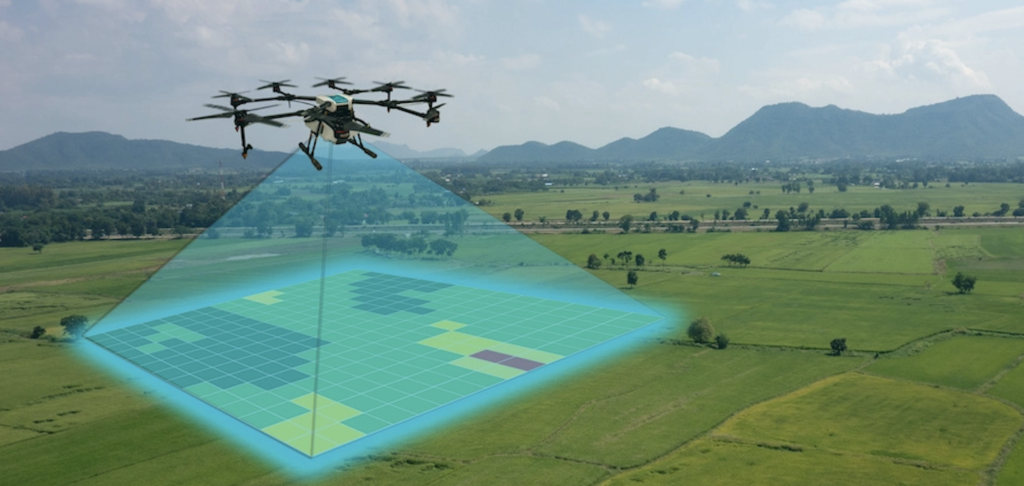

One way that businesses are already using drones and will continue to use future drones is to survey land. Future drones equipped with cameras and sensors can quickly and accurately map out large areas of land, making it easier for companies to plan construction projects or determine property boundaries. Surveying with drones is much faster than traditional methods, which require teams of people walking the area on foot or using expensive equipment like helicopters.
Cost-effective: Traditional methods of surveying can be expensive due to the need for specialised equipment and personnel. With drones, surveys can be conducted quickly and at a lower cost.
Faster Data Collection: UAVs are capable of collecting vast amounts of data in a short amount of time. This allows surveyors to analyse information more efficiently, saving both time and money.
Better Accuracy: Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras or LiDAR sensors provide accurate topographical mapping without having to physically access difficult terrain areas that may pose safety risks such as cliffs or steep slopes.
To operate drones effectively during surveys requires skilled drone pilots who understand how to collect data safely while producing quality results. Drone operators must also possess knowledge about the specific regulations governing their use when operating within national airspace systems (NAS).
V-TOL’s (Vertical Take-off and Landing) range is designed specifically for professional applications like geospatial mapping, precision agriculture, inspection work among others. V-TOL offers advanced features including GNSS RTK accuracy down to centimetre level allowing users an unprecedented level of detail on maps they create using V-TOL’s proprietary software suite.
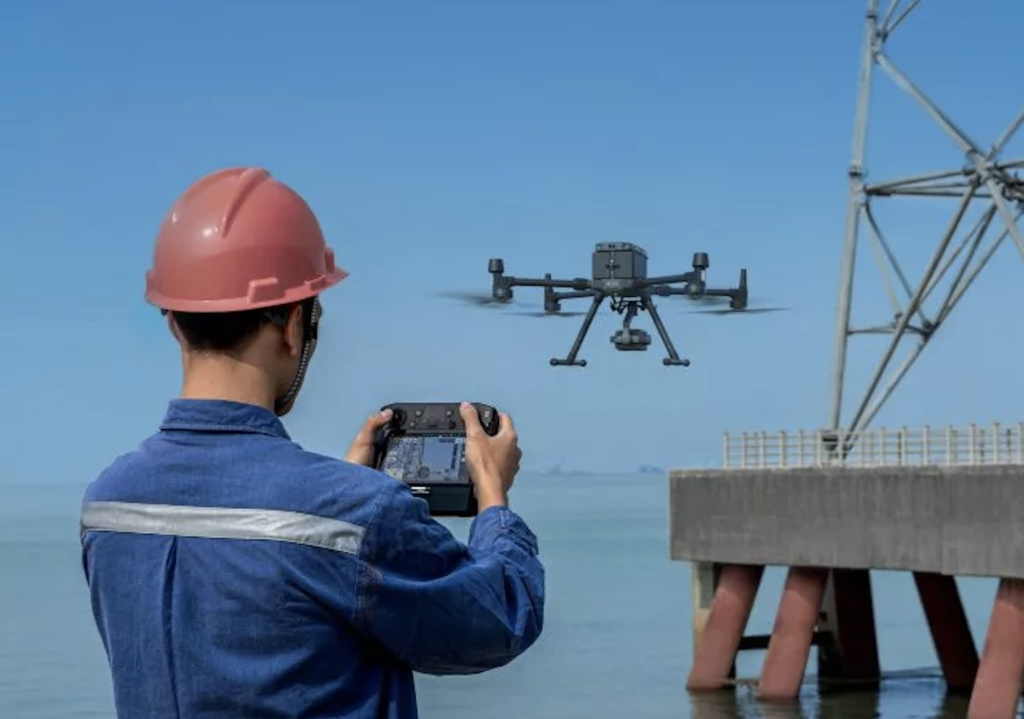

Also used to inspect infrastructure such as bridges and buildings. By flying a drone around a structure, inspectors can get a close-up view without putting themselves at risk. This method is not only safer but also more cost-effective than sending humans up to do inspections.
Safety: One of the most significant benefits of using drones is safety. Instead of sending inspectors to dangerous or hard-to-reach areas, drones can be flown over these locations to capture high-quality images and videos without putting anyone at risk.
Ease-of-use: Drones are easy to operate compared to traditional methods like scaffolding or cranes. They require minimal setup time and can cover large areas quickly with high accuracy.
Cost-effectiveness: Using drones for inspections is cost-effective because it reduces labor costs associated with traditional inspection methods such as hiring equipment operators or renting heavy machinery.
Data Accuracy: Drones equipped with GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) technology provide accurate data that helps engineers make informed decisions about maintenance needs or repairs required on infrastructure systems.
The following are some examples where drone usage has been proven effective in inspecting infrastructure:
Bridges: Drones equipped with cameras help capture detailed imagery from all angles while flying around bridge structures. This method allows inspectors to identify any potential issues such as cracks, corrosion, or other structural defects that may not be visible from ground level.
Pipelines: Aerial thermal imaging by drones is an effective way to detect leaks in pipelines. The drone’s camera captures thermal images that help identify temperature changes along the pipeline, which can indicate a leak or other issues.
Power Lines: Drones equipped with LiDAR technology (Light Detection and Ranging) are used to inspect power lines. This method helps inspectors locate potential faults such as damaged insulators, conductors, or vegetation growing too close to the power line.
The use of future drones for infrastructure inspection has become increasingly popular due to their efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. We can certainly expect more innovative ways of using drones in different industries as drone technology continues to advance
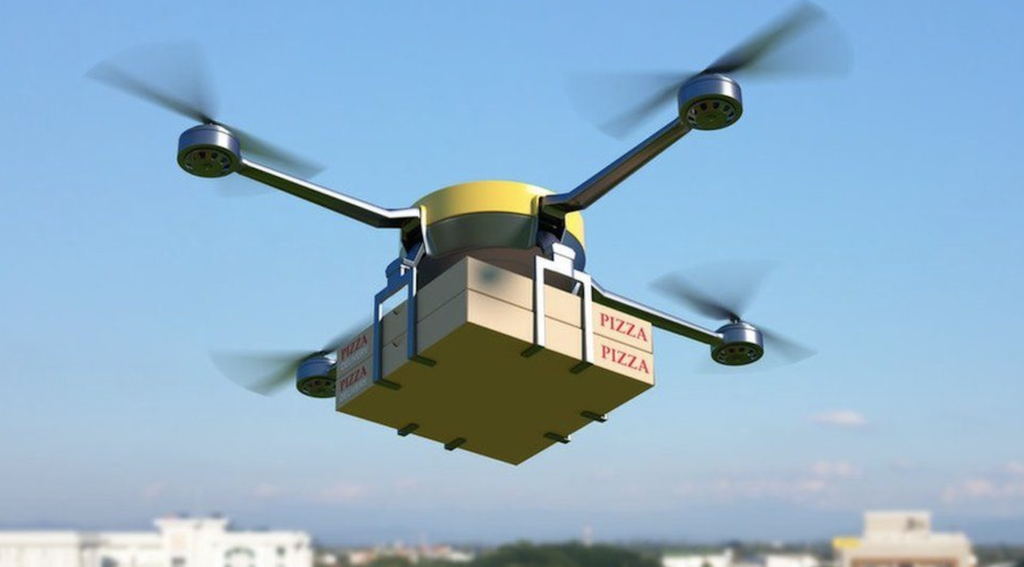

In addition to surveying and inspection services, some companies are experimenting with using drones for delivery services.
Future drones are thought to be utilised in many ways, however, Amazon has already been testing their Prime Air service which aims at delivering packages within half an hour after placing an order online while other companies such as UPS have partnered with Matternet Inc., whose technology enables deliveries from medical suppliers straight into hospitals’ landing pads via small quad-copters carrying payloads weighing up to five pounds.
Using drones for last-mile delivery can reduce costs associated with traditional ground transportation while also improving efficiency by reducing traffic congestion and lower carbon emissions.
In a typical drone delivery system, a package is loaded onto a drone at a warehouse or distribution centre (sometimes by other autonomous drones). The UAV then takes off and flies to its destination using GPS navigation systems. Once it reaches the designated location, it drops off the package and returns back to base.
Faster Deliveries: Drones can make deliveries within minutes compared to hours taken by traditional modes of transportation like trucks or bikes.
Eco-Friendly: Drone-based deliveries emit less carbon than conventional means of transport thereby reducing pollution levels significantly.
Cheaper Costs: Using drones could reduce costs associated with fuel consumption and maintenance expenses since they don’t require drivers/operators which could lead up-to cost reduction overall.
The implementation of future drone delivery systems faces several challenges including regulatory issues around airspace management and safety concerns related with commercial flights and UAVs’ operations near populated areas. There’s also concern about security risks posed by hackers who might try stealing sensitive data during drone operations.
Despite these challenges, the use of future drones in delivery services is expected to grow rapidly as companies continue to invest in developing new technologies and solutions that address these concerns.

Some industries including media houses use UAVs fitted with high definition cameras capable of capturing aerial footage, thus enabling them to produce stunning visuals that were previously impossible.
Drones equipped with cameras have opened up new possibilities for aerial photography and videography. With UAVs, photographers can capture stunning images from unique perspectives that were previously impossible without expensive equipment like helicopters or cranes.
This has made them a valuable tool for real estate agents looking to showcase properties, filmmakers creating movies or commercials, and even wedding photographers seeking creative shots.
In addition to capturing breathtaking landscapes from above, drones are also useful tools for filmmakers who want to add dynamic shots to their movies or documentaries.

Drones are also being used in the farming industry to monitor crops and livestock. By using drones, farmers can quickly identify areas of their fields that need attention, such as those affected by pests or droughts. This allows them to take action before it’s too late.
Overall, drones have proven themselves to be a valuable tool for businesses across many industries. As future drone technology continues to improve and regulations become more relaxed around drone usage, we can expect even more innovative uses for these unmanned aerial vehicles.
The agricultural industry has also begun using drones extensively. By equipping unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with sensors capable of measuring temperature, moisture levels, soil conditions, crop health, and more, farmers can gather data about their crops quickly without having to physically inspect each field themselves. This information allows them to make informed decisions about irrigation schedules or fertiliser applications, which ultimately leads to higher yields at lower costs.
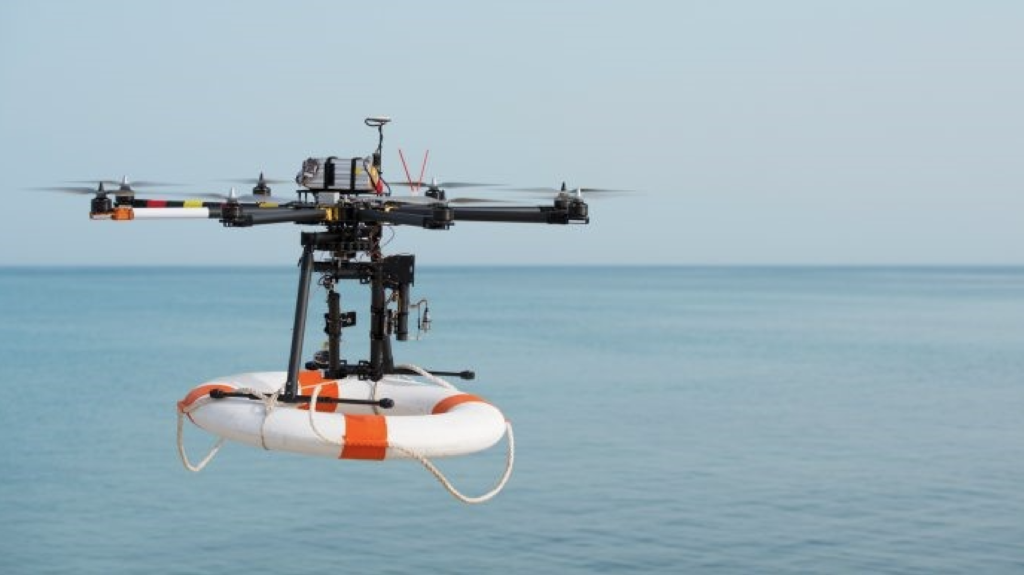

Drones are invaluable in search and rescue operations following natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, or fires due to their high-resolution cameras and thermal imaging capabilities.
Equipped with high-resolution cameras and thermal imaging capabilities, they can quickly scan large areas for survivors. They also provide real-time footage to the control centre, which helps strategise the rescue efforts effectively. Learn more about drones in search and rescue operations here.
Rapid Deployment: Drones can be launched quickly from almost any location without the need for a runway or specialised equipment.
Aerial View: The bird’s eye view provided by drones allows rescuers to cover large areas of terrain quickly while also providing detailed images that may not be visible from the ground.
Night Vision: Many drones are equipped with thermal imaging cameras that allow them to detect body heat even at night, making it easier to locate individuals who may be lost or injured.
Drones are not meant to replace traditional search and rescue methods but rather complement them. Ground teams still play an essential role in conducting searches on foot while using GPS technology. However, when combined with drone technology, these searches become more efficient due to increased visibility of hard-to-reach areas such as cliff-sides or dense forests where human access is limited.
In recent years, there has been an increase in the use of unmanned aerial systems (UAS) for commercial purposes such as surveying land or inspecting infrastructure. As this trend continues, we will likely see more advanced drone technologies being used during search and rescue missions including VTOL drones and GNSS satellites.
Furthermore, as drone technology continues to evolve, we may see more advanced features being added such as AI-powered object recognition software that can detect people in distress or even medical supplies delivery systems that could be used during emergency situations.
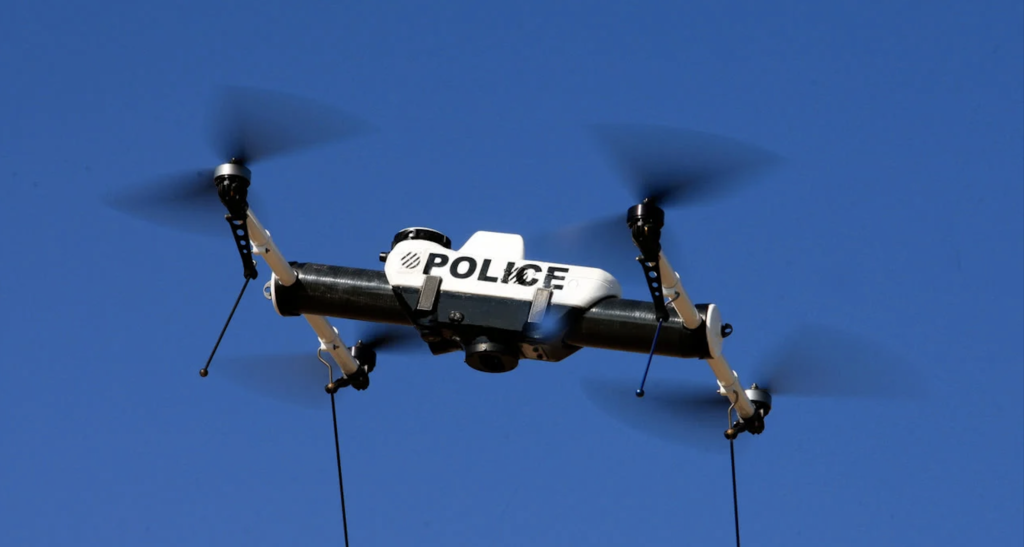

The use of drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), has been a topic of discussion for many years. While the military has used drones for reconnaissance and surveillance purposes, civilian drone usage is on the rise. Drones are being utilised by businesses, entrepreneurs, and even law enforcement agencies.
In recent years, police departments have started using drones to help catch criminals. One of the main advantages of using a drone is that it can cover large areas quickly and efficiently. This means that police officers can search for suspects without having to put themselves in harm’s way.
Future drones equipped with high-resolution cameras will provide real-time video footage from above, allowing law enforcement officials to track suspects’ movements or monitor crime scenes from afar. They are especially useful during hostage situations where officers need to assess the situation before taking action.
While there are benefits to using drones in law enforcement operations, there are also concerns about privacy violations. Critics argue that constant surveillance by drones could lead to an infringement of citizens’ rights to privacy.
In addition, there is concern over who controls these devices since they could potentially be hacked or misused if not regulated properly. Moreover, drones could be used to conduct unauthorised surveillance on private property or individuals.
As the use of drones in law enforcement continues to grow, it is important that proper regulations are put in place to protect citizens’ privacy and ensure these devices are being used for legitimate purposes only.
Law enforcement agencies are increasingly using drones to monitor public gatherings, pursue suspects, or investigate crime scenes. The aerial view provided by these devices allows officers to assess situations from a safe distance without putting themselves at risk. In some cases, drones equipped with speakers are even used for crowd control during protests.

Scientific research has always been an important aspect of human progress. With the advent of technology, we have been able to make great strides in our understanding of the world around us. One such technological innovation that has made a significant impact on scientific research is drones.
One major advantage that drones offer for scientific research is their ability to access areas that are otherwise inaccessible to humans. For example, researchers can use drones equipped with cameras or sensors to explore remote locations like mountaintops, glaciers, and even active volcanoes without putting themselves at risk.
This opens up new avenues for exploration and discovery in fields like geology, ecology, and climatology. Scientists can now collect data from places they couldn’t before, which helps them gain a better understanding of natural phenomena such as climate change or volcanic activity.
Drones also play a crucial role in wildlife conservation efforts by providing researchers with a non-invasive way to study animal behaviour patterns without disturbing their habitats. By using thermal imaging cameras mounted on drones or GPS tracking devices attached to animals’ collars, scientists can monitor endangered species populations more effectively than ever before.
Archaeologists are also using drones to help them map out ancient sites more accurately. By taking aerial photographs or creating detailed 3D models of archaeological sites, researchers can gain a better understanding of how people lived in the past.
Drones have revolutionised scientific research by providing us with new ways to explore our world. From studying animal behaviour patterns to mapping out ancient sites, drones offer scientists an unprecedented level of access that was previously impossible.
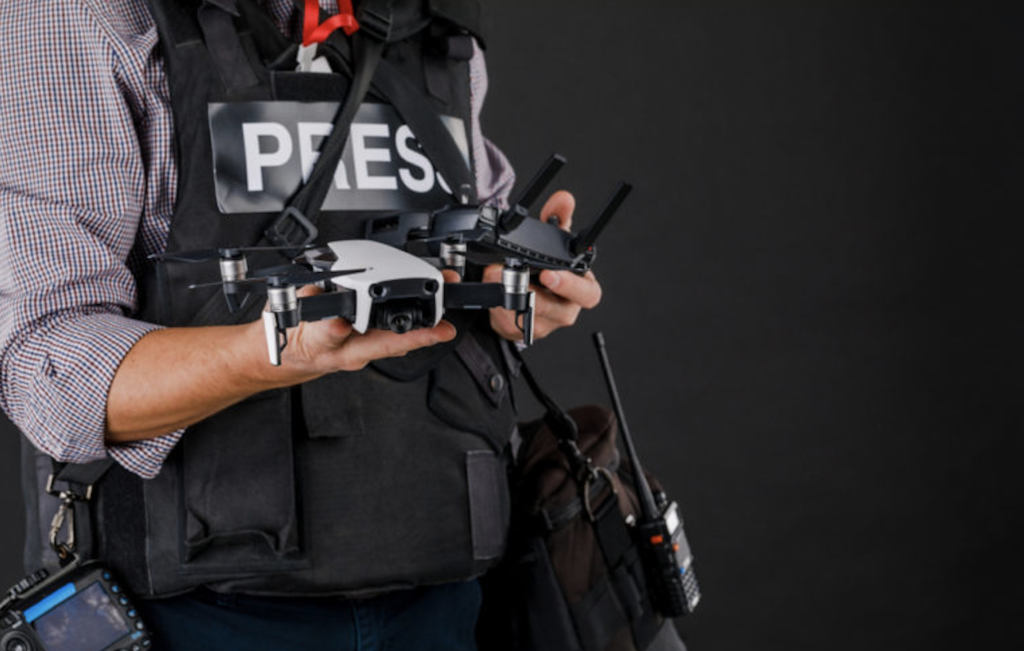

Journalism has always been about finding new and innovative ways to tell stories. With the advent of drone technology, journalists now have a powerful tool at their disposal that allows them to capture footage from vantage points previously inaccessible.
The use of drones in journalism has revolutionised the way news is reported. Journalists can now capture aerial footage that provides a unique perspective on events as they unfold. This type of coverage was once only possible with expensive helicopters or planes, but drones have made it more accessible and cost-effective.
Improved Safety: Drones allow journalists to cover dangerous situations without putting themselves in harm’s way. For example, during natural disasters like hurricanes or wildfires, reporters can use drones to get an aerial view of the affected areas without risking injury.
Better Coverage: Drones provide a bird’s eye view that traditional cameras cannot match. This allows for better coverage and storytelling by providing context and scale that would be impossible otherwise.
The future looks bright for drone journalism as more media outlets embrace this technology. In addition to capturing footage, drones are also being used for data collection and analysis which will help journalists uncover new stories and trends.
Data Collection: Drones equipped with sensors can collect data on everything from air quality to traffic patterns which can be used by journalists for investigative reporting or trend analysis.
New Storytelling Techniques: As drone technology advances, so too will the ability for journalists to tell even more compelling stories. With advancements in virtual reality and 360-degree video, viewers will be able to experience events like never before.
The use of drones in journalism has changed the way news is reported by providing a new perspective on events as they unfold. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more exciting developments in this field.
New-age journalists often rely on UAV footage when covering news events, providing viewers a bird’s eye view of what’s happening.
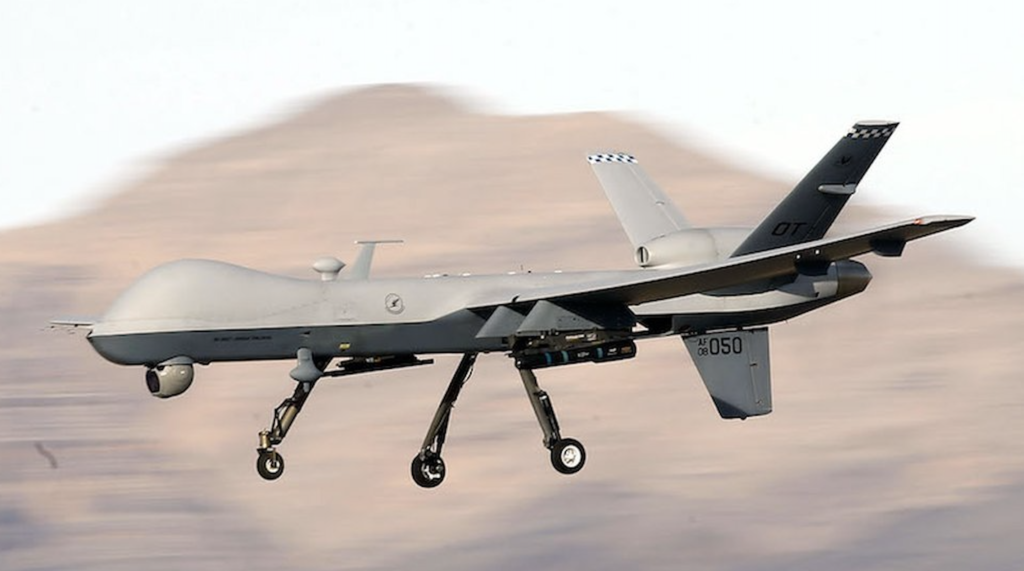

The use of future drones or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) has revolutionised modern warfare. Drones are used by the military for a variety of purposes, including reconnaissance, surveillance, and targeted strikes.
Cost-effective: Compared to traditional manned aircraft, armed drones are less expensive to operate and maintain.
Safety: The use of drones reduces the risk to human pilots who would otherwise be flying over hostile territory.
Precision: With advanced sensors and targeting systems on board, drones can deliver precise strikes against enemy targets with minimal collateral damage.
The use of drone technology has had a significant impact on modern warfare. One major advantage is that it allows militaries to gather intelligence without putting soldiers’ lives at risk. This means that troops can stay out of harm’s way while still gathering critical information about enemy positions and movements.
In addition, drone technology has made it possible for militaries to carry out precision airstrikes against high-value targets with minimal civilian casualties.
In recent years, there have been concerns raised about the ethics surrounding the use of drones in warfare. Critics argue that because they can be operated remotely from thousands of miles away from their target area by operators sitting behind computer screens, they make it easier for governments to engage in wars without accountability or transparency as well as increase civilian deaths due to inaccurate targeting systems among other reasons.
However, proponents counter-argue these claims saying that “drone strikes” have saved countless lives compared to conventional methods where innocent civilians could easily be caught in the crossfire.

While drones are often used for commercial purposes, they can also be a fun and exciting hobby. Drone enthusiasts around the world enjoy using their unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for recreational activities such as photography, videography, and even racing.
Drone racing leagues have emerged as a new sport where pilots race their custom-built quad-copters through obstacle courses at high speeds.
The popularity of drone racing leagues has exploded in recent years. These competitions involve pilots flying small drones through obstacle courses at high speeds while wearing first-person view goggles that show them what the drone sees. The races can take place indoors or outdoors and require skilful manoeuvring to avoid obstacles like hoops or gates.
Many people find this sport thrilling because it combines the excitement of piloting with technology in an adrenaline-fuelled race against other competitors. Some popular drone racing leagues include:
The Drone Racing League (DRL)
MultiGP
Rotor Rush
Drones have emerged as versatile and indispensable tools in various fields, ranging from search and rescue missions to scientific research, law enforcement, military operations, deliveries, surveying, and business operations. They offer numerous advantages such as improved safety, as well as increased efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and precise data collection.
While regulatory and security concerns still exist at present, the potential benefits of drone technology are undeniable. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect even greater advancements and innovative applications from future drones.
Exploring the world of drones opens up opportunities for both personal interests and professional endeavours, making it an exciting time to embrace this transformative technology.
But why stop here? Click this to check out more about drones!
Related Post’s

How high can drones fly? Well, we leave no stone unturned in answering exactly that! From hobbyists, to commercial and military drones too.
How Far Can Drones Fly? Learn about flight times, legalities, and drone usage across industries here in this article.

Navigate New York drone laws with confidence. Understand federal, state, and local regulations for safe commercial and recreational drone use.